Difference between water content and water activity
The difference between water content and water activity
1. Water content? Water activity? What's the difference?
Moisture content refers to the amount of water contained in the total weight of the item itself. Take coffee beans as an example: it is generally believed that green beans with a moisture content between 10 and 12% are conducive to storage and coffee roasting. However, the moisture content includes free water that can be directly used by microorganisms and bound water locked in the structure of the green beans. Therefore, it can only be used as one of the reference factors for the state of the green beans. Generally, a halogen lamp moisture balance is used to measure the moisture content.
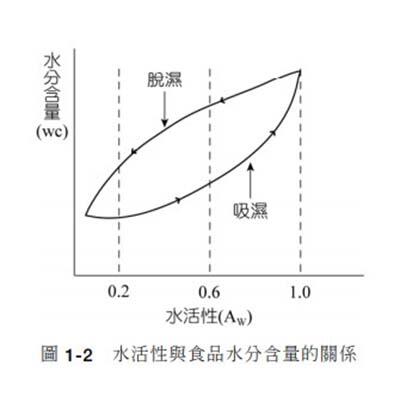
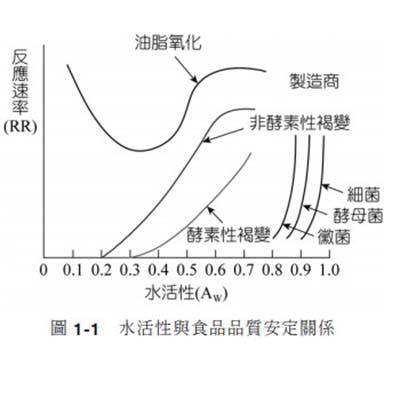
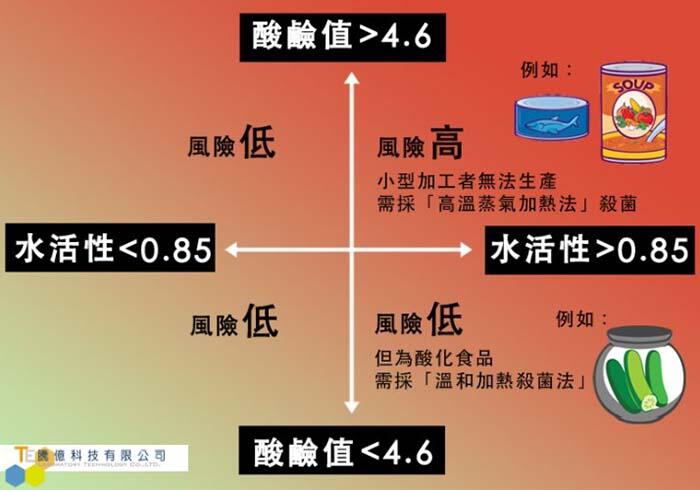
To increase your understanding of the current condition of green beans, you can refer to another parameter commonly used in the food industry: Water Activity (AW). As mentioned above, free water can be directly used by microorganisms, and vapor pressure is the pressure value generated after the free water evaporates. The definition of AW is the ratio of the vapor pressure of an object to the vapor pressure of pure water under the same conditions. The value is between 0 and 1. The closer it is to 1, the more water in the object can be used by microorganisms. For green beans, it means that they are more likely to be affected by mold, bacteria, etc., thereby reducing the quality and flavor.
2. How much water activity is appropriate?
The recommended water activity for green beans is generally between 0.4 and 0.6. If it is higher than 0.6, it means that there is more free water available for microorganisms, and there is a risk of infection by mold and fungi for the green beans. If it is lower than 0.4, it may be that the green beans are over-dried when processed, or the environment is too dry during transportation and storage, which affects the original flavor and subsequent coffee roasting.
3. How to control water activity?
Before controlling AW, it is best to use a water activity meter to understand the current AW value of the green beans so that you can predict the changes in AW after environmental changes. Continuous monitoring and control of the storage environment, such as temperature, humidity and light, will affect the moisture content and AW of the green beans. Compared with the burlap bags commonly used to package green beans, it is recommended to use airtight packaging or containers to store green beans. Reducing the impact of the environment on the green beans can also stabilize AW and reduce changes.
Neither AW nor moisture content can fully indicate whether the green beans have been properly dried, stored, or transported. However, it can be considered as the current state of the green beans, whether there is a risk of microbial influence, etc. It can also serve as a reference indicator for subsequent green bean storage and quality.