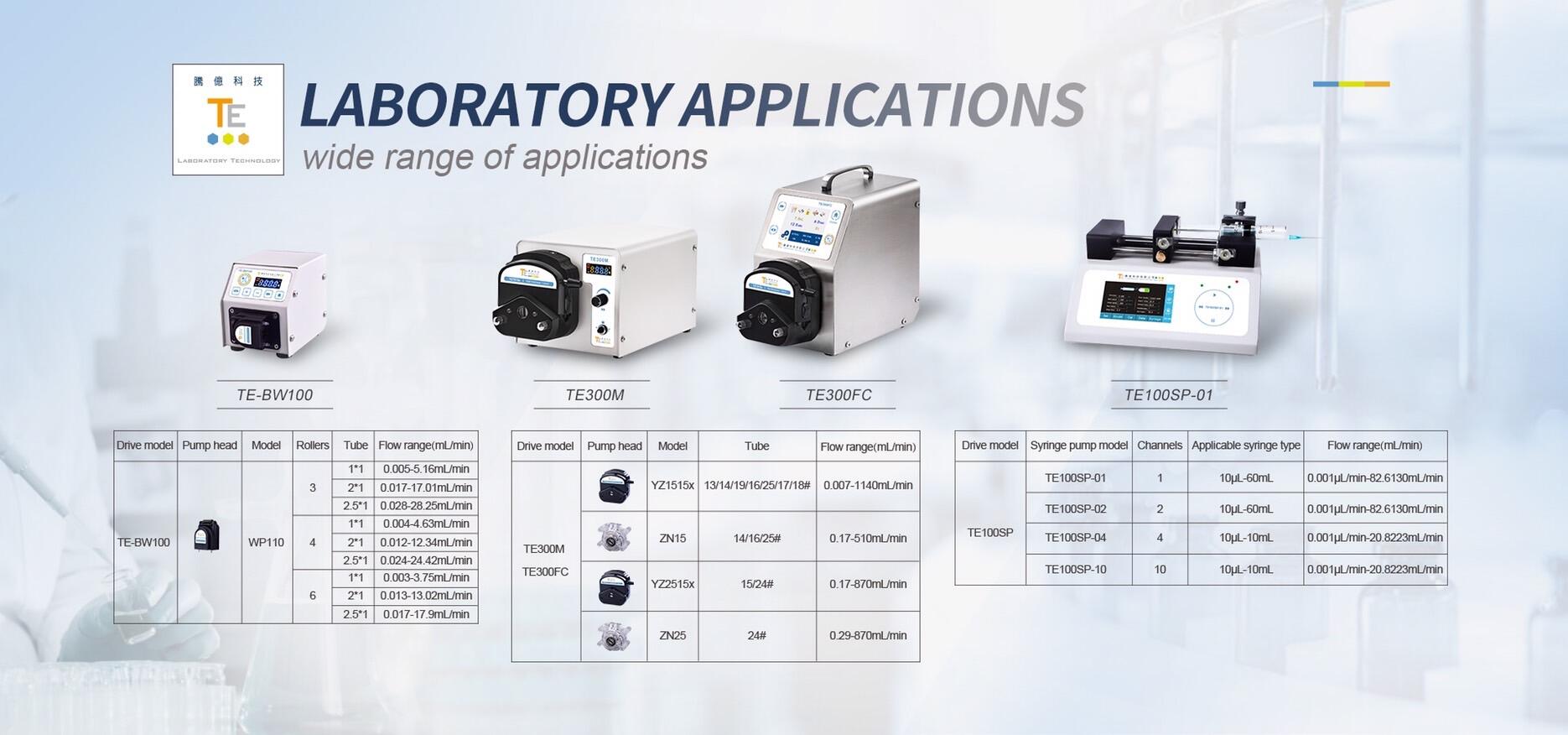
Principles of peristaltic pumps and injection pumps
Principles of peristaltic pump and injection pump
Injection pump:
Injection pump is a common instrument used in life science research to uniformly inject trace amounts of liquid. It controls the smooth operation and precise positioning of the syringe piston through a precision device. Using a high-precision syringe pump in an experiment not only saves costs, but also minimizes the number of experimental errors and avoids inefficient work.
Features of the injection pump
The injection pump is an intelligent injection device that can accurately, evenly and continuously inject drugs into the body, strictly control the dosage of drugs, ensure the best effective concentration of drugs, reasonably adjust the injection speed of drugs, continuously infuse various urgently needed drugs, and reduce the occurrence of complications.
1 Accuracy:
Built-in syringes of various brands to ensure infusion accuracy.
2 Safety:
Extension tube detachment alarm system: monitors the application status at all times to prevent the risk of invalid infusion and blood outflow from the patient, and protects the patient's safety. Blockage detection system: Blockage level, reducing subcutaneous tissue necrosis or irritation caused by special medication output outside the blood vessel, ensuring the safety of infusion. Blockage pressure release function: When the extension tube or pump is blocked, the injection pump will release the pressure immediately to reduce the risk of intravenous injection.
3 Ease of use:
Numeric keypad: allows for more convenient and quick operation.
Application of injection pump in microprocess
Microfluidics is a revolutionary interdisciplinary research that integrates biotechnology, chemistry, physics and engineering, and has broad application prospects. Microfluidics is the science of precisely controlling and manipulating the behavior of microfluidics at the microliter to picoliter scale, enabling a variety of experiments and functions in submillimeter channels and other structures. In fact, microfluidics is the cutting-edge core technology that will lead future fluid research.
Microfluidics is a revolutionary interdisciplinary research that integrates biotechnology, chemistry, physics and engineering, and has broad application prospects. Microfluidics is the science of precisely controlling and manipulating the behavior of microfluidics at the microliter to picoliter scale, enabling a variety of experiments and functions in submillimeter channels and other structures. In fact, microfluidics is the cutting-edge core technology that will lead future fluid research.
Applications:
Lab-on-a-chip
Organ-on-a-chip
DNA analysis
PCR amplification
Ultra-high throughput bioassays
Cell sorting
Point-to-point therapeutic diagnostics
Proteomics
Biosensing/BioMEMS
Microreactors
Microdroplet formation
Pump options range from single to multi-channel, as well as pressure control, and flow rates from picoliters to microliters.
A peristaltic pump is a liquid delivery device that can control the flow rate. It can stably control the flow rate of the fluid, deliver the fluid without pollution, and is simple and cheap to maintain. It has the advantages of high delivery accuracy, strong corrosion resistance, small shear effect, simple operation and easy maintenance. Therefore, peristaltic pumps can be used in any scenario that requires precise and quantitative delivery of fluids, such as medical equipment, analytical instruments, water treatment, environmental protection equipment, coatings and paints, printing and inkjet printing, food and beverage, chemical engineering, biopharmaceuticals, process industries and many other industries. It is often used in scientific research laboratories for cell tissue transportation, specimen decolorization, perfusion, liquid chromatography analysis, and acidic or alkaline solution transportation.
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
2. Low shear conveying: The fluid is not sheared, making it easy to convey shear-sensitive fluids.
3. High delivery accuracy: The characteristics of the positive displacement pump allow the pump to output a fixed amount of fluid each time it rotates, so it can be used for metering and quantitative delivery.
4. Self-priming dry operation: Peristaltic pumps can be operated dry to transport gas, liquid, gas-liquid mixture, and fluid containing solid particles. The maximum diameter of the solid particles is 30% of the hose diameter. The vacuum created by the peristaltic pump makes the pump self-priming, eliminating the need to prime the pump with water before starting.
5. Stop valve function without siphon: the pump tube is cut off by the roller, and the valve is not required to prevent backflow and siphon.
6. Equal flow rate delivery in forward and reverse directions: By changing the direction of the motor, the forward and reverse directions of the liquid can be switched, and the forward and reverse flow rates are equal.
7. Simple maintenance and easy cleaning: The hose is the only consumable. Since there are no valves and seals, it is easy to install and operate, and the hose can be quickly replaced on site.
8. It can transport viscous liquids such as salad dressing and glutinous rice glue, as well as abrasive and corrosive liquids, and can also transport liquids containing solid particles.
Disadvantages of peristaltic pump characteristics:
1. The hose needs to be replaced regularly: The service life of the elastic hose is fixed and needs to be replaced regularly.
2. The output fluid has pulses: Due to the peristaltic extrusion principle, the output liquid will produce pulses. If smooth delivery is required, the pulse frequency can be increased by increasing the number of pressure wheels to reduce the fluid pulse amplitude. Increasing the number of wheels will shorten the wheel spacing of the hose, reduce the hose rebound amplitude, and reduce the flow rate. At the same time, increasing the number of wheels will increase the wear of the hose and reduce the life of the hose.
Peristaltic pump head and pressure:
The head of a peristaltic pump depends on the pressure of the peristaltic pump. Generally, a small OEM peristaltic pump uses a 1.6mm peristaltic pump hose or a 2.4mm peristaltic pump hose. Its discharge pressure can generally reach about 1KG. Under the premise of stable peristaltic pump flow, its head can reach 5-7 meters. Pumps using peristaltic pump hoses with wall thicknesses of 3.3mm, 4.8mm and 6.3mm will have higher pressures and higher lifts.
Flow rate of peristaltic pump:
Flow rate is an important parameter of the pump, which is affected by many factors, the main factors are:
1. Inner diameter of hose: the larger the inner diameter, the greater the flow rate.
2. Pump rotation diameter: The larger the diameter, the greater the flow rate.
3. Pump speed: The higher the speed, the greater the flow rate.
4. Number of pressure wheels: The more wheels there are, the smaller the flow rate is, the more pulses are generated, and the smaller the pulse amplitude is.
5. Fluid viscosity, specific gravity and suction range: The higher the fluid viscosity, specific gravity and suction range, the lower the rebound speed and rebound rate of the hose, the lower the conveying efficiency and the smaller the flow rate.
6. Fluid head and flow rate: When the head exceeds the rated pressure of the pump, the pressure generated by the liquid will squeeze the pipe wall, causing the pipe wall to become thinner, destroying the closed cut-off state of the hose and causing backflow.
Classification of peristaltic pumps:
1. Complete peristaltic pump: refers to a complete product that can be used after plugging in a power source and has the functions of start/stop, forward/reverse rotation, speed and flow regulation. Complete sets of peristaltic pumps are generally used in laboratories and factories.
2. OEM peristaltic pump: OEM peristaltic pump is mainly used by instrument manufacturers to integrate into instruments and equipment for supporting use, and the user needs to provide power supply and drive control circuit. OEM peristaltic pump = pump head + motor components, cannot be directly operated and used, and users need to assemble and debug them by themselves.
Peristaltic pump selection:
Peristaltic pump composition = peristaltic tube + peristaltic pump head + driver
Peristaltic pump is composed of three parts: peristaltic tube, peristaltic pump head and driver. So the steps for selection are as follows:
1. Determine whether you need a complete set of peristaltic pumps or OEM pumps.
2. Determine the flow size.
3. Determine the pump head: based on the required number of channels, appearance, tube replacement method, accuracy, lifespan, and appearance.
4. Determine the drive control part: based on the conveying accuracy, life, appearance and control method.
5. Determine the peristaltic pump tube: Select the peristaltic pump tube material based on the type of liquid being transported and the required hose life.
Chemical compatibility of peristaltic pumps:
1. The fluid in the pump only contacts the inner surface of the peristaltic pump hose, without valves and seals, and will not contact any other parts of the pump. When the peristaltic pump is working, the roller constantly squeezes the hose. The hose needs to maintain resilience to pump the liquid normally. The pump tube and the transported liquid cannot produce changes in chemical and physical properties. Therefore, the peristaltic pump cannot use non-elastic tubes such as PTFE.
2. Common materials for peristaltic pump tubes include nitrile rubber (NBR), Hypalon, fluororubber (Viton), silicone, PVC, EPDM, EPDM + polypropylene (such as Santoprene), polyurethane and natural rubber. Silicone tubing is most widely used in peristaltic pumps. Viton has good corrosion resistance, but its life is relatively short. TPE materials such as PharMed BPT have a longer lifespan. To understand the working life of various peristaltic pump hoses, you can check the life table of peristaltic pump hose pump tubes.
3. The chemical compatibility of the transported fluid and hoses of different materials can be obtained by consulting the chemical compatibility table or by conducting a chemical compatibility experiment.
Product details: https://www.te-lab-equipment.com.tw/pump